Isolate, activate, and expand T cells
Rely on the same proven technology platform throughout mouse and human stages of your T cell research. Obtain a 100- to 1000-fold expansion of T cells within 9–14 days, with no need for feeder cells or antigen presenting cells (APCs). T cells exhibit properties comparable to in vivoactivated T cells.
- For Mouse research—Dynabeads Mouse T-Activator CD3/CD28
- For Human in vitro research—Dynabeads Human T-Expander CD3/CD28
- For Clinical research—Dynabeads CD3/CD28 CTS
Preserve T cell viability and optimal immune function
Dynabeads CD3/CD28 CTS (formerly known as Xcyte Dynabeads and Dynabeads ClinExVivo CD3/CD28) was developed to optimize ex vivo T cell expansion in translational research while preserving T cell viability and optimal immune function.
Designed to mimic in vivo activation and expansion, these ready-to-use Dynabeads are coated with antibodies directed against the TCR/CD3 and co-stimulatory CD28 receptors that are required for optimal T cell expansion.
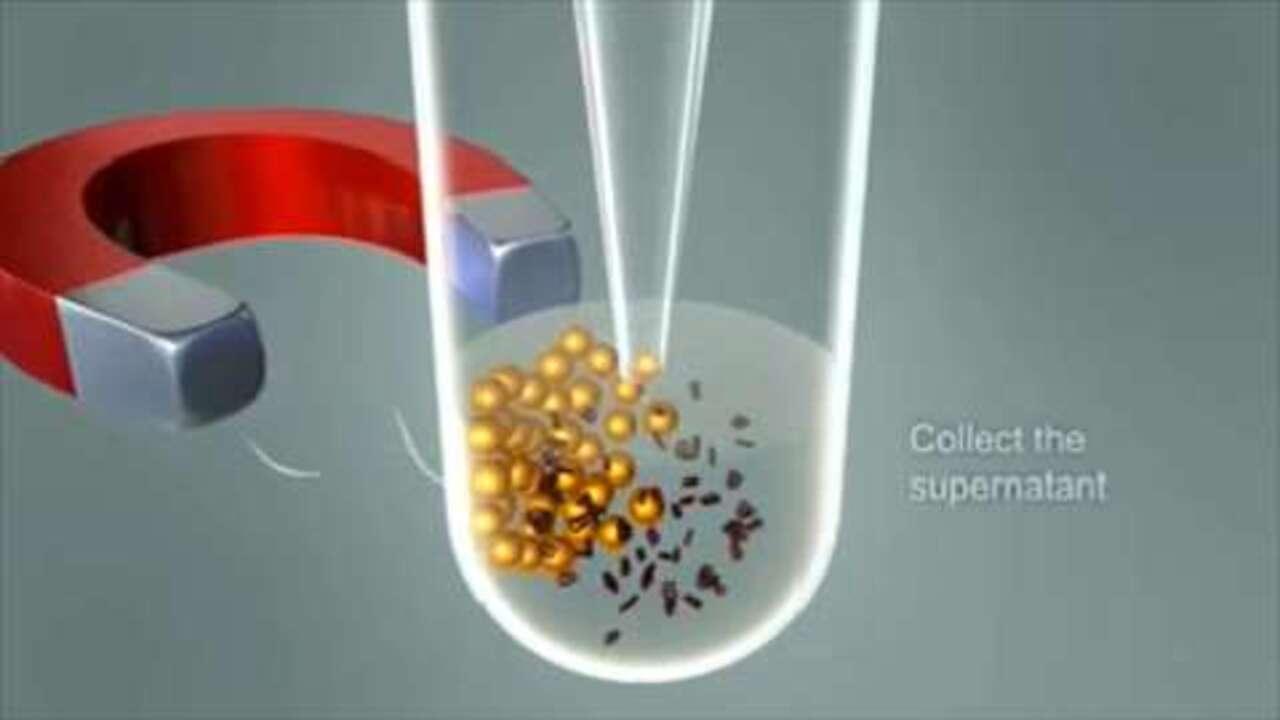
The DynaMag CTS magnet is developed for optimal performance with the Dynabeads CD3/CD28 CTS technology, and allows you to work with large sample sizes (up to 10 L).

Figure 1. Diagram compares T cell activation with in vivo activation with Dynabeads.
Legal and Regulatory
In USA, Dynabeads CD3/CD28 CTS are available for clinical use only under an approved IND application. A Device Master File is held at the US Food and Drug Administration for cross-referencing in Investigational New Drug (IND) applications.
References on T cell expansion
- Almåsbak H, Aarvak T, Vemuri MC (2016) CAR T cell therapy: A game changer in cancer treatment. J Immunol Res 2016:5474602. doi: 10.1155/2016/5474602.
- Smith C, Økern G, Rehan S et al. (2015) Ex vivo expansion of human T cells for adoptive immunotherapy using the novel Xeno-free CTS Immune Cell Serum Replacement. Clin Transl Immunology 4:e31. doi: 10.1038/cti.2014.31.
- Teschner D, Wenzel G, Distler E et al. (2011) In vitro stimulation and expansion of human tumour-reactive CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes by anti-CD3/CD28/CD137 magnetic beads. Scand J Immunol 74:155–64.
- Rasmussen AM, Borelli G, Hoel HJ et al. (2010) Ex vivo expansion protocol for human tumor specific T cells for adoptive T cell therapy. J Immunol Methods 355:52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.02.004.
- Neurauter AA, Bonyhadi M, Lien E et al. (2007) Cell isolation and expansion using Dynabeads. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 106:41–73.
- Neurauter AA, Aarvak T, Norderhaug L et al. (2006) "Chapter 30—Separation and Expansion of Human T cells" in Cell Biology: A Laboratory Handbook. (Elsevier, Inc., ed. J E Celis).
- Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Sifri-Steele C et al. (2003) A phase I trial of CD3/CD28-activated T cells (Xcellerated T cells) and interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:3562–3570.
Related T cell expansion and isolation product areas
Using Dynabeads for T cell expansion
Dynabeads allow for specific capture of biomolecules while undesired molecules don't bind. Gentle magnetic separation leaves unbound molecules in the solution and bead-bound molecules ready for downstream analysis.
See Dynabeads Cell Isolation & Expansion support within the Cell Analysis Support Center for tips, troubleshooting help, and resources.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.