Online and downloadable materials for NanoDrop spectrophotometers
The manuals, brochures, application and technical notes, videos, webinars, and other resources in this section will help you get the most out of your Thermo Scientific NanoDrop One/OneC, Eight, or Lite Plus spectrophotometer, or 3300 fluorospectrometer.
For similar materials for NanoDrop 2000/2000c, 8000, Lite, and 1000 spectrophotometers, see Resources for discontinued NanoDrop instruments at the bottom of this page.
Featured NanoDrop spectrophotometer resources
Simple, easy, and fast nucleic acid and protein quantification
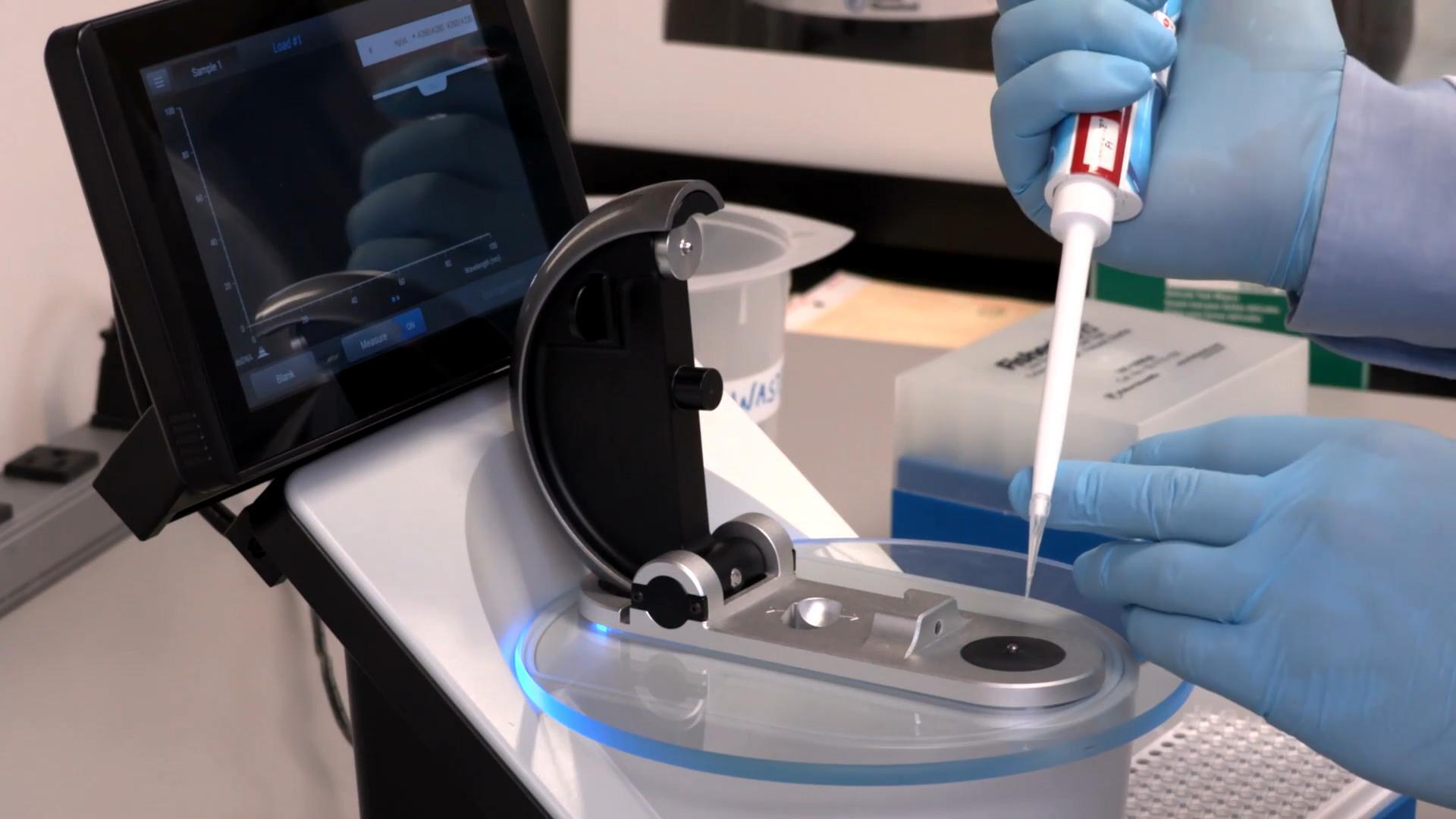
Perhaps the most striking feature of NanoDrop quantitation is how simple and easy it is to use. The pioneering NanoDrop pedestal system helps minimize sample volume and simplifies operation. Simply pipet a drop of your DNA, RNA, or protein sample—as little as 1.0–2.0 µL—on the pedestal and pull down the arm. No cuvettes or capillaries are needed and the results appear in seconds.
Accurate nucleic acid and protein quantification via UV absorbance
NanoDrop spectrophotometers work on the principle of ultraviolet-visible spectrum (UV-Vis) absorbance. Nucleic acids absorb light with a peak at 260 nm. Purified proteins absorb light at a peak of 280 nm, while peptides and proteins that lack tryptophan and tyrosine residues absorb at a peak of 205 nm. Many contaminants left over from extraction protocols absorb at either 280 nm or 230 nm.
Generation of optical signal
The photometric measurement of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and proteins is based on their intrinsic absorptive properties. When an absorption spectrum is measured, nucleic acids absorb light with a characteristic peak at 260 nm.
Quantitation of nucleic acids and protein samples
Concentrations of nucleic acids and proteins are calculated automatically from their measured absorbance values at the desired wavelength using the Beer-Lambert equation, where:
- c = concentration in molar (M)
- A = UV absorbance in absorbance units (AU)
- e = wavelength-dependent molar absorptivity coefficient (or extinction coefficient) in M-1cm-1
- L = light path length in cm
One implication of the Beer-Lambert equation is that for low-concentration samples, a longer path length results in greater accuracy and signal-to-noise ratio. NanoDrop instruments automatically optimize the length of the liquid column for maximum accuracy across a wide concentration range.
Accuracy of NanoDrop One dsDNA quantitation validated against a reference instrument. A series of dsDNA dilutions was prepared ranging from 3–28,000 ng/µL and quantitated spectrophotometrically at 260 nm on the NanoDrop One and Evolution 300 spectrophotometers. (A) A linearity comparison across the entire instrument concentration range was plotted. The regression line demonstrates that the NanoDrop One dsDNA concentration results were well aligned (R2 = 0.9991) with the values obtained on the reference Thermo Scientific Evolution 300 Spectrophotometer. (B) A closer look at the linearity comparisons at the low concentration range (from 3–495 ng/μL) was also plotted. The regression line shows a close correlation (R2 = 1) to the Evolution 300 results and superb linearity at the lower end of the detection range. For method and more detailed data, see the NanoDrop One nucleic acid technical note.
Purity analysis for nucleic acid and protein samples
Purity of a sample can be assessed using ratios of absorbance of one wavelength to another. Sample contamination may result in overestimation of the nucleic acid concentration and/or inaccuracies in downstream processes or measurements.
Key purity ratios for UV absorbance
Ratio |
Analyte |
Considered “pure” | Factors that can cause abnormal ratios |
A260/A280 |
Nucleic acids |
DNA: ~1.8 |
Contaminants indicated by low ratios: · Proteins · Residual phenol or other reagents used in extraction protocol |
A260/A230 |
Nucleic acids |
DNA/RNA: ~2.0–2.2 |
Contaminants indicated by low ratios: · Proteins · Carbohydrate carryover (often a problem with plants) · Residual phenol from nucleic acid extraction · Residual guanidine (often used in column-based kits) · Glycogen used for precipitation Factors indicated by high ratios: · Problems with Blank measurement |
A260/A280 |
Proteins |
~0.6 |
Contaminants indicated by high ratios: · Nucleic acids |
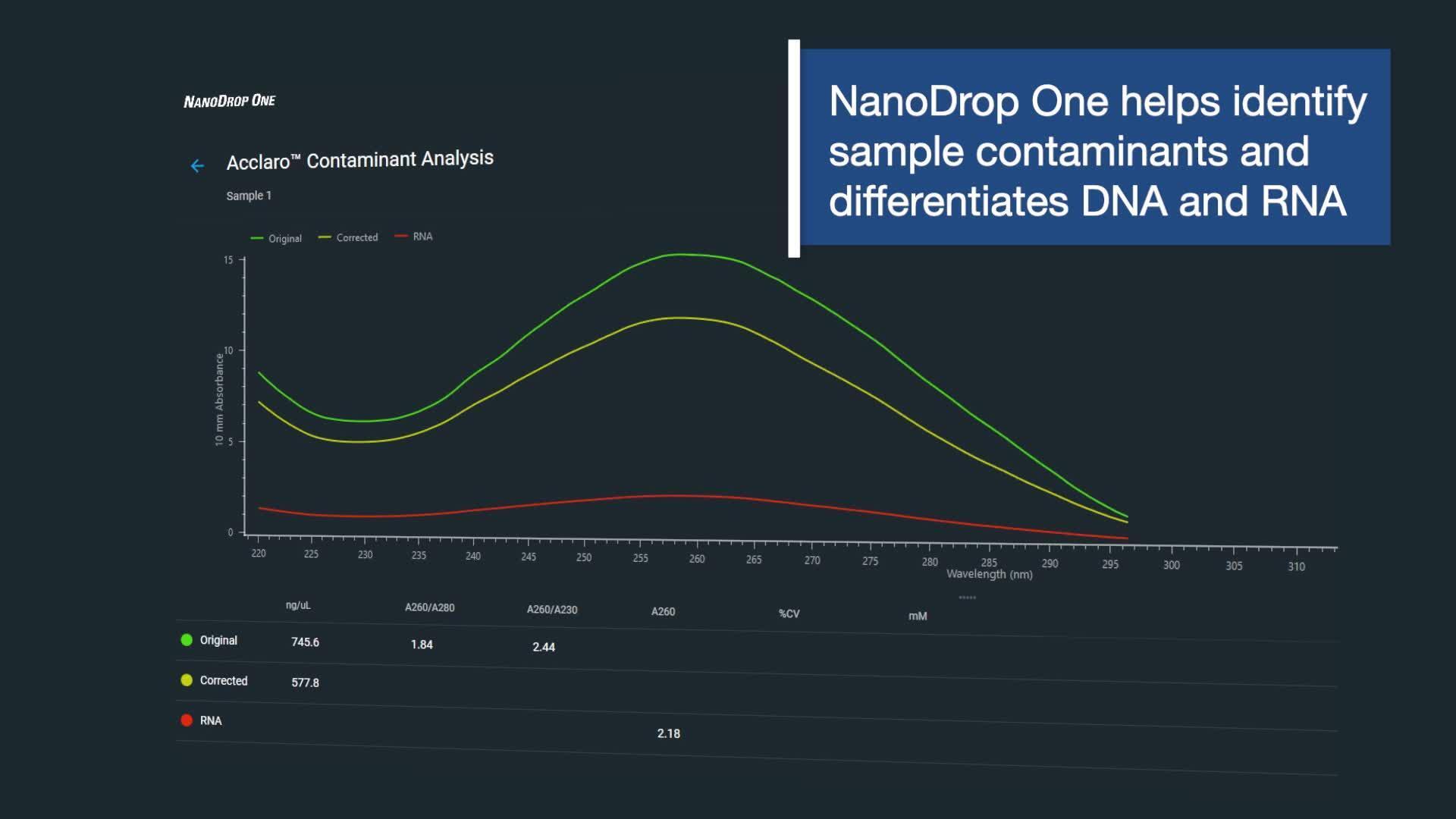
Beyond purity ratios, impurities can alter spectral profiles, shifting peaks and troughs as shown in the figure.
Contaminants cause shifts in spectral profiles
Spectra of purified DNA without contamination (A, red) and of the same sample contaminated with guanidine (B, green) and phenol (C, brown).
NanoDrop instruments that run Acclaro Sample Intelligence software can use this kind of whole-spectrum data to identify contaminants, as described in Features.
Documents for the NanoDrop One/Oneᶜ Spectrophotometer
Documents for the NanoDrop Eight Spectrophotometer
NanoDrop spectrophotometer videos
NanoDrop spectrophotometer webinars
Support and educational resources for NanoDrop spectrophotometers
For technical support in the United States and Canada, please call 877-724-7690, option 4 or email NanoDrop technical support at nanodrop@thermofisher.com. For international assistance, please email nanodrop@thermofisher.com or contact your local NanoDrop distributor.
Many technical support questions can be answered by consulting the documentation, literature, videos, and webinars above. In addition, our free online educational materials include these Learning Centers and pages covering spectroscopy, protein biology, and nucleic acid quantification.
Resources for discontinued NanoDrop instruments
Find manuals, brochures, application and technical notes, videos, and other resources to help you get the most out of your NanoDrop 2000/2000c, 8000, Lite, or 1000 spectrophotometer.
Resources for the NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer
Resources for the NanoDrop 2000/2000c Spectrophotometer
Resources for the NanoDrop 3300 Spectrophotometer
Resources for the NanoDrop 8000 Spectrophotometer
Resources for the NanoDrop Lite Spectrophotometer
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.