In forensic casework, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is useful in the context of challenging samples that fail to produce an autosomal STR profile due to their high copy number per cell. Traditional Sanger sequencing using capillary electrophoresis (CE) is generally limited to the sequencing of the hypervariable region. The Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel is an innovative approach to mitochondrial DNA sequencing specifically developed for forensic applications. This mtDNA tiling approach, using amplicons that are only 163 bp average length, assists with obtaining optimal mtGenome coverage from highly compromised, degraded samples such as hair shafts, teeth, and bones. The Precision ID mtDNA Control Region Panel is based on the same tiling approach used in the Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel. This targeted control region panel spans the entire 1.2-kb control region, which encompasses HV-I, HV-II, and HV-III, with the same optimal small amplicon design ideal for performance with degraded forensic samples. In addition, the panel design leverages primer degeneracy in known variable regions to ensure robust performance across diverse population samples. The Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel, using the control region data for analysis, is approved for inclusion in the US National DNA Index System (NDIS) CODIS database.
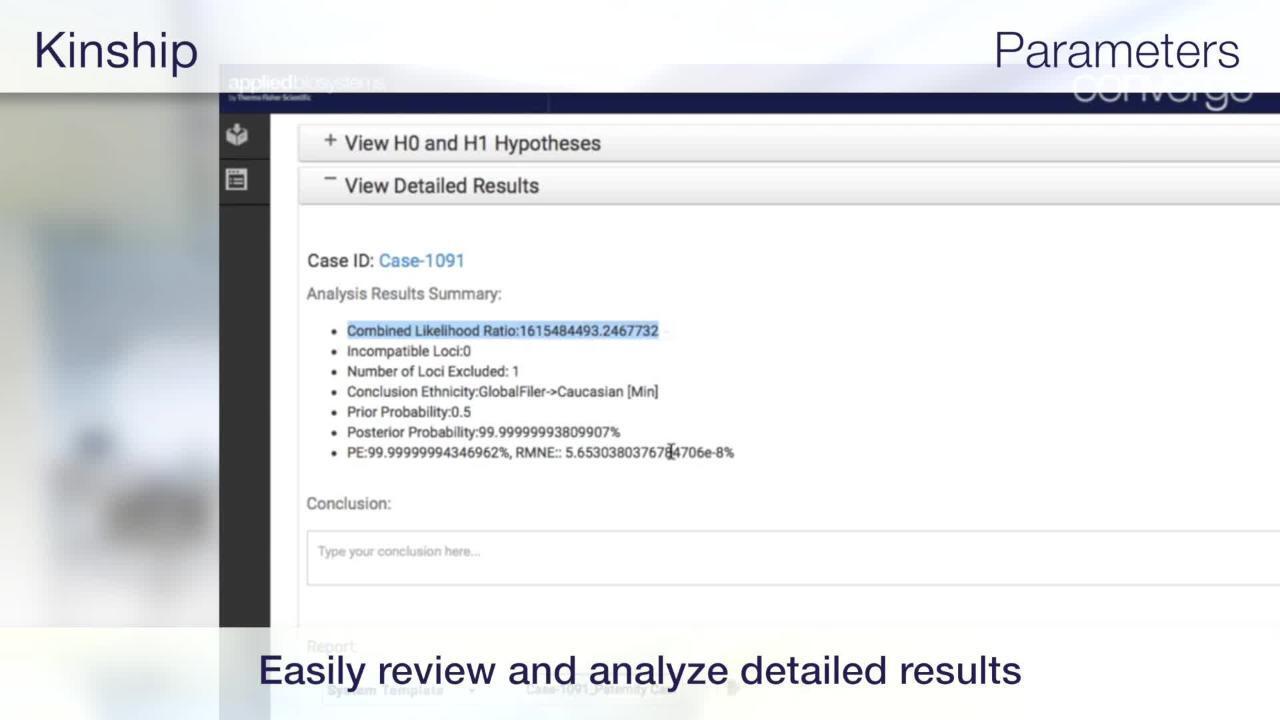
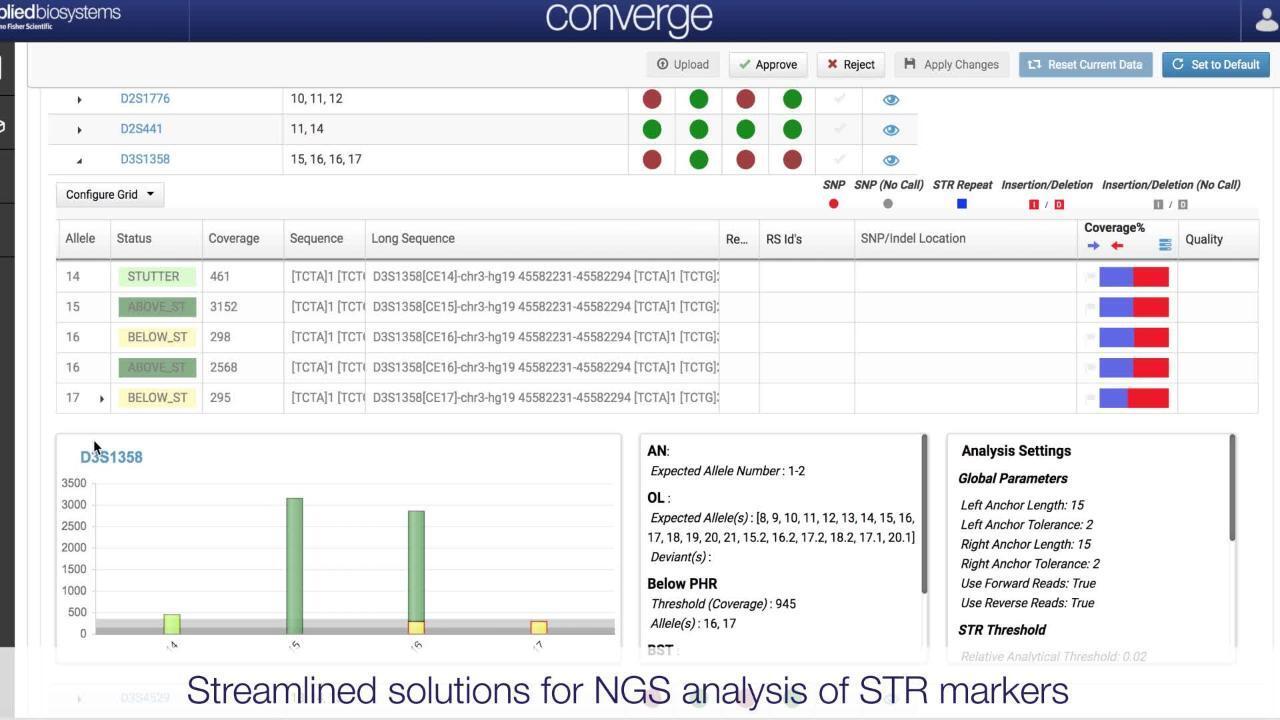
Analysis of the mtGenome can be challenging due to complex alignments, the presence mtDNA heteroplasmy, and insertions and deletions present throughout the genome that may impact the accuracy of variant calling. The automated mtDNA NGS analysis pipeline integrates various sources of knowledge for mtDNA variation, including PhyloTree and EMPOP, to provide fine-tuned alignments and variant calls that avoid the pitfalls of standard algorithms. Laboratories interested in more advanced analysis and reporting of mtDNA types can obtain haplotype and haplogroup information, along with quantitative assessments for point and length heteroplasmies, down to ~10% assuming a minimal sequencing coverage of >100x. NUMTs are insertions of mtDNA sequence into the nuclear genome and can be non-specifically (or non-intentionally) amplified with the mtDNA genome, presenting as a possible source of contamination. The Converge Software NGS Data Analysis module contains NUMT statistics and can detect and filter this type of contamination.