FIGURE: 1 / 2
Human IFN-gamma Protein (PHC4031) in Functional
Product Details
PHC4031
Species
Published species
Expression System
Amino acid sequence
Molecular weight
Class
Type
Purity
Endotoxin concentration
Activity
Conjugate
Form
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Product Specific Information
Carrier-Free
Target Information
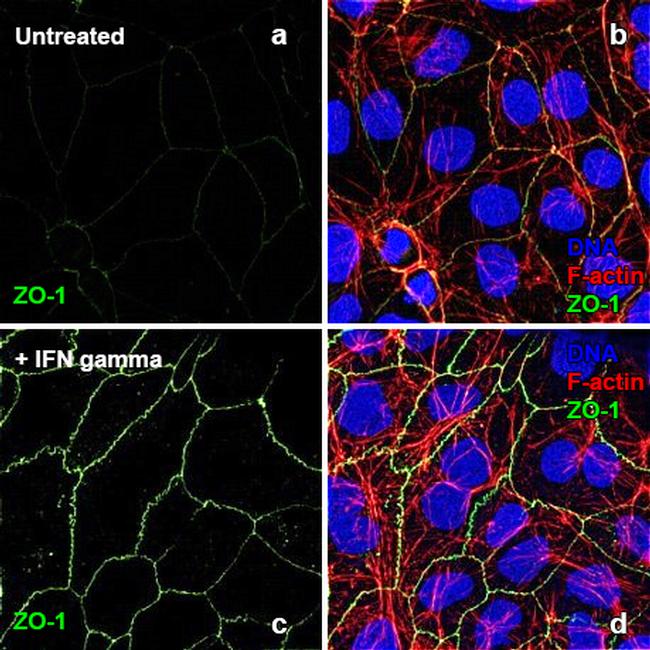
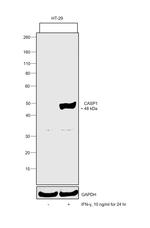
IFN gamma (Interferon gamma, Type II interferon) is a macrophage activation factor, and immune interferon that is produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells in response to antigens, mitogens, Staphylococcus enterotoxin B, phytohemaglutanin and other cytokines. IFN gamma is a dimeric protein consisting of two 146 amino acid subunits. IFN gamma is a glycoprotein that exists, functionally, as a homodimer of approximately 45 kDa. On SDS-PAGE, IFN gamma appears as a combination of 25, 20 and minor 15.5 kDa bands as a result of differential glycosylation. The biological activity of the IFN gamma homodimer is highly species specific. Human IFN gamma does not show cross-reactivity with mouse. IFN gamma function includes the following: antiviral activity, tumor antiproliferative activity, induction of class I and II MHC, macrophage activation, and enhanced immunoglobulin secretion by B lymphocytes. IFN gamma is involved in cytokine regulation and also acts synergistically with other cytokines. Activation of IFN gamma takes place through binding of IFN gamma receptor I and II, and activating the JAK-STAT pathway. IFN gamma does not show any homology with IFN alpha or IFN beta but human IFN gamma shows about 40% sequence homology with mouse IFN gamma. IFN gamma is upregulated by IL2, FGF basic, EGF and downregulated by vitamin D3 or DMN. IFN gamma gene mutations are associated with aplastic anemia.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: H-IFN-g; IFN γ; IFN-gamma; IFN-y; IFNγ; Immune interferon; Interferon gamma; Interferon y; Interferon γ; interferon, gamma; Interferonγ; M-IFN-g; R-IFN-g
Gene Aliases: IFG; IFI; IFNG
UniProt ID: (Human) P01579
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 3458

We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support