Invitrogen
NOTCH1 Monoclonal Antibody (mN1A), PE, eBioscience™
FIGURE: 1 / 1
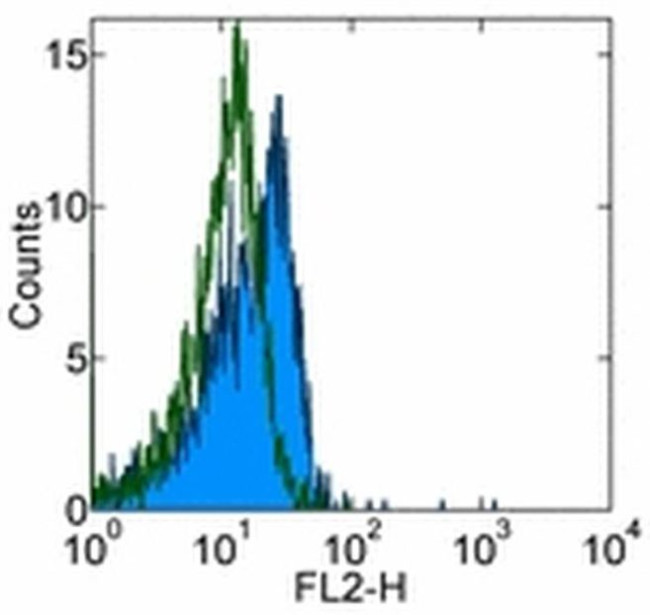
NOTCH1 Antibody (12-5785-82) in Flow
Product Details
12-5785-82
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Recommended Isotype Control
Class
Type
Clone
Conjugate
Excitation/Emission Max
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Description: The Notch family of transmembrane receptors controls cell-fate decisions during the development of many organs in a wide variety of species. After binding its ligand, the Notch receptor is cleaved in its transmembrane domain, and the resulting intracellular domain dissociates from the membrane and translocates to the nucleus, where it is able to suppress the expression of lineage-specific genes by interacting with transcriptional repressors. The mN1A antibody reacts with the intracellular domain of mouse and human Notch1, but not with Notch2, 3, or 4. The mN1A antibody has a low affinity for the full-length (unprocessed or heterodimeric cell surface) forms of Notch1. In the mouse, Notch mRNA is expressed in mouse hematopoietic cells of the fetal liver and adult thymus and bone marrow. In the thymus, Notch1 protein is detected in CD4-CD8- (double-negative) and CD4-CD8+ (single-positive) thymocytes. Studies of Notch1-transgenic cells and Notch1-null mice indicate that the receptor is involved in the regulation of lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis.
Applications Reported: This mN1A antibody has been reported for use in intracellular staining followed by flow cytometric analysis.
Applications Tested: This mN1A antibody has been tested by intracellular staining and flow cytometric analysis of mouse thymocytes using the Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set (Product # 88-8824-00)and protocol. Please refer to Best Protocols: Protocol A: Two step protocol for (cytoplasmic) intracellular proteins located under the Resources Tab online. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.25 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Excitation: 488-561 nm; Emission: 578 nm; Laser: Blue Laser, Green Laser, Yellow-Green Laser.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Target Information
The notch gene belongs to a family of epidermal growth factor (EGF) like homeotic genes, which encode transmembrane proteins with a variable number of cysteine-rich EGF-like repeats in the extracellular region. Four notch genes have been described in mammals: Notch1, Notch2, Notch3 and Notch4(Int-3), which have been implicated in the differentiation of the nervous system and other structures. The EGF-like proteins Delta and Serrate have been identified as ligands of Notch1. Mature Notch proteins are heterodimeric receptors derived from the cleavage of Notch pre-proteins into an extracellular subunit (NEC) containing multiple EGF-like repeats and a transmembrane subunit including intracellular region (Ntm).
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
How to use the Panel Builder
Watch the video to learn how to use the Invitrogen Flow Cytometry Panel Builder to build your next flow cytometry panel in 5 easy steps.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: major type A protein; Motch A; mT14; Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; Notch 1; Notch gene homolog 1; Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated; p300; RP23-306D20.12; RP23-306D20.12-001; Translocation-associated notch protein TAN-1; transmembrane receptor Notch1
Gene Aliases: 9930111A19Rik; AOS5; AOVD1; hN1; lin-12; Mis6; Motch; N1; NOTCH1; TAN1
UniProt ID: (Human) P46531, (Mouse) Q01705
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 4851, (Mouse) 18128

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support