Invitrogen
IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody (RN17), Functional Grade, eBioscience™
Product Details
16-7473-82
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Recommended Isotype Control
Class
Type
Clone
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
Description: The monoclonal antibody RN17 reacts with and inhibits the bioactivity of mouse IL-17F. IL-17F is a 37kD homodimer of the IL-17 family and a signature Th17 marker. Of all the six IL-17 family members, IL-17F and IL-17A share the strongest homology (50% amino acid identity), and the two genes are located in the same chromosomal region. Recent studies have demonstrated coordinated regulation of IL-17A and IL-17F during Th17 differentiation. Expression of IL-17F and IL-17A has been detected in activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes, specifically by activated human CD4^+ T cells. In addition to IL-17A, differentiated Th17 cells also produce IL-17F and IL-22 upon re-activation. Like IL-17A, IL-17F has been linked with inflammatory diseases. IL-17F and IL-17A expression has been observed in tissue samples from various autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma. IL-17F treatment of airway epithelium, vein endothelial cells, and fibroblasts has been reported to induce expression of IL-6, IL-8, GRO-alpha, ENA-78, TGF-beta, MCP-1, G-CSF, GM-CSF, and ICAM-1.
Like IL-17A, IL-17F is a disulfide-linked homodimeric glycoprotein. The IL-17F homodimer includes a classical cysteine knot motif, which is found also in the TGF-beta, BMP, and NGF superfamilies. The presence of the cysteine knot motif suggested the possibility of a heterodimeric structure, as was reported for TGF-beta and inhibin/activin. Recent reports confirm that co-expression of IL-17F and IL-17A in HEK293 cells results in the formation of biologically active IL-17F/IL-17A heterodimers, in addition to the IL-17F homodimers and IL-17A homodimers. Moreover, activated human CD4^+ T cells were found to produce the IL-17A/F heterodimer, along with the corresponding homodimers. In comparing the relative potency of IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-17A/F, all three were found to induce GRO-alpha secretion; IL-17A was most potent, followed by IL-17A/F heterodimer, then IL-17F (100fold lower than IL-17A). In the mouse, the IL-17A/F heterodimer (alone or in synergy with TNF-alpha) was found to regulate the expression of IL-6 and KC (mouse homolog of human GRO-alpha); this was found to be dependent on IL-17RA and TRAF6.
Applications Reported: This monoclonal antibody reacts with and inhibits the bioactivity of mouse IL-17F.
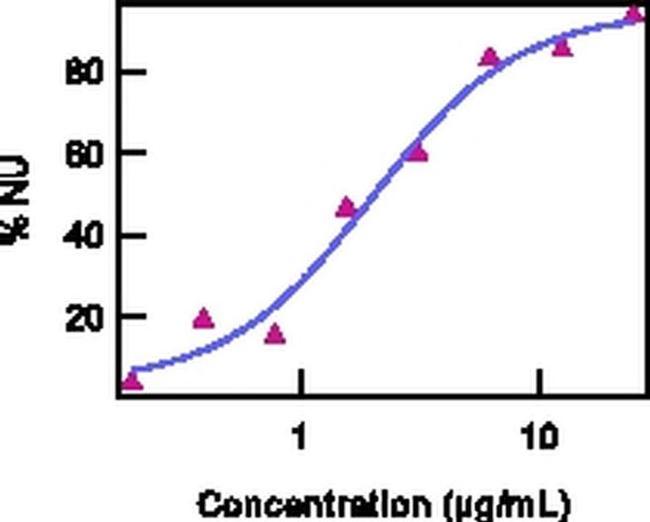
Applications Tested: The ND50 of RN17 as measured by the inhibition of mouse IL-6 induction in NIH/3T3 cells is 1-6 µg/mL in the presence of 4 µg/mL of recombinant mouse IL-17F. Neutralization dose will vary depending on assay method, cytokine concentration, and cell type. This antibody should be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Storage and handling: Use in a sterile environment.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Endotoxin Level: Less than 0.001 ng/µg antibody, as determined by LAL assay.
Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC.
Target Information
IL-17F (Interleukin 17F, CTLA-8)) is a cytokine belonging to the IL-17 family that is produced by inflammatory cells such as activated T cells, mast cells, and basophils. IL-17F is involved in allergic airway inflammation, and can induce several cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in bronchial epithelial cells, vein endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and eosinophils. IL-17F may be secreted as a homodimer, or a heterodimer with IL17A. It acts by binding to the type I receptor, IL-17R, aiding recruitment of monocytes and neutrophils at the site of inflammation by increasing chemokine production. IL-17F also stimulates induction of other pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and IL-8, and reports strongly suggest the involvement of IL-17 in several chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. TGF-beta (differentiation) and IL-23 (expansion) are required for induction and maintenance of Th17 (IL-17 producing) cells, which in turn induce the other pro-inflammatory cytokines. IL-17F is produced, and exists, as a homo-dimer, with homology to a herpes virus early protein, is one of the six members (IL-17A-F) of this cytokine family, and is well characterized and highly expressed by activated effector memory T cells. IL-17F has been found to inhibit the angiogenesis of endothelial cells and induce endothelial cells to produce IL2, TGFB1/TGFB, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: IL-17F; ILN; Interleukin; Interleukin-17F; interleukin-24; Interleukin17F; mutant IL-17F
Gene Aliases: C87042; IL-17F; Il17f
UniProt ID: (Mouse) Q7TNI7
Entrez Gene ID: (Mouse) 257630

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support