FIGURE: 1 / 3
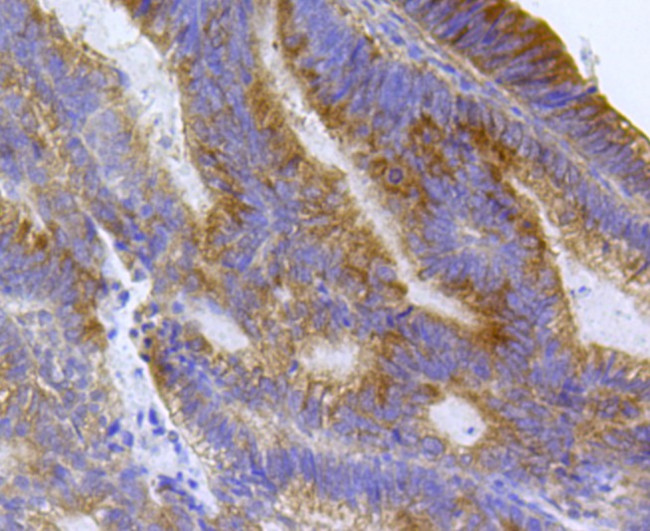
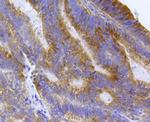
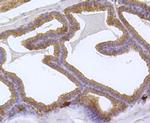
EEA1 Antibody (MA5-44618) in IHC (P)
Product Details
MA5-44618
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Clone
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Target Information
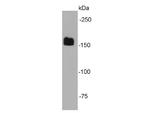
Early endosomal antigen 1 (EEA1) is a 162 kDa membrane bound protein component specific to the early endosome and is essential for fusion between early endocytic vesicles. Early endosomes are cytoplasmic compartments which fuse with endocytic vesicles for redistribution of extracellular compounds to alternate destinations. Zinc-finger-like domains, reminiscent of those found in nucleic acid binding proteins, are located in the amino and carboxyl-terminal domains of EEA1. The carboxyl-terminal zinc-finger-like-domain is conserved in several other non-nuclear proteins, some of which are also involved in intracellular protein trafficking. In addition, this domain is an authentic zinc-binding domain and is critical to the intracellular localization of EEA1. Membrane association of EEA1 has been shown dependent on phosphatidyl 3-kinase activity, inhibitors of which cause EEA1 to dissociate from early endosomes.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: Early endosome antigen 1; early endosome antigen 1, 162kD; early endosome-associated protein; Endosome-associated protein p162; Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 2
Gene Aliases: A430109M19Rik; B230358H09Rik; EEA1; MST105; MSTP105; ZFYVE2
UniProt ID: (Human) Q15075, (Mouse) Q8BL66
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 8411, (Rat) 314764, (Mouse) 216238

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support